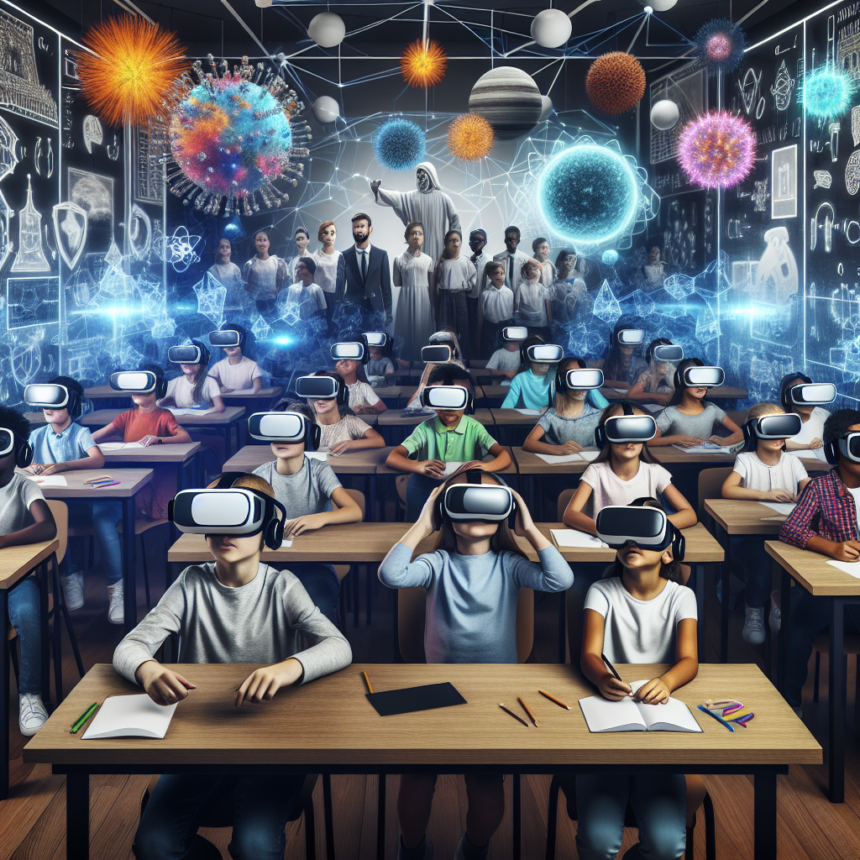
In recent years, the landscape of education has undergone significant changes, driven by advancements in technology. One of the most groundbreaking innovations is virtual reality (VR), which has started to make waves in classrooms worldwide. As educators seek new ways to engage students and enhance learning experiences, VR offers immersive environments that traditional teaching methods cannot replicate. This article explores how virtual reality is transforming education and revolutionizing the classroom experience.
What is Virtual Reality in Education?
Virtual reality in education refers to the use of VR technology to create simulated environments where students can engage in a range of learning activities. By wearing VR headsets, students can step into different scenarios, from exploring the solar system to participating in historical reenactments. This technology promotes active learning, allowing students to observe, interact, and manipulate virtual objects in a way that enhances their understanding and retention of knowledge.
Enhancing Engagement and Motivation
One of the most immediate benefits of incorporating VR into the classroom is heightened engagement. Traditional teaching methods often struggle to capture students’ attention, especially with newer generations accustomed to high-tech experiences. VR provides a captivating alternative, stimulating students’ curiosity and encouraging them to participate more actively.
For example, a biology class can come alive as students virtually explore the human body, witnessing the inner workings of organs and systems in a way that textbooks cannot replicate. This level of immersion not only captures students’ interests but also makes learning more enjoyable, fostering a deeper connection to the material.
Fostering Experiential Learning
Experiential learning is a cornerstone of effective education. Virtual reality allows students to engage in hands-on activities that reinforce theoretical concepts. For example, a history class can transform into a time travel adventure where students witness significant events firsthand, gaining insights that facilitate a more profound understanding of the subject matter.
Moreover, VR enables students to practice skills in safe, controlled environments. In healthcare education, for instance, medical students can use VR simulations to perform surgeries without the risk of harming patients. Such experiences empower learners to build confidence and competence before applying their knowledge in real-world scenarios.
Collaborating in a Virtual Space
Virtual reality also breaks down geographical barriers, enabling collaboration among students from different regions or even different countries. Multi-user VR environments encourage cooperative learning, allowing students to work together on projects while feeling as though they’re in the same room.
Imagine a science class where students from various parts of the globe can come together in a virtual lab to conduct experiments, share results, and collaborate on findings. This global collaboration not only enriches the learning experience but also prepares students for a world where teamwork and communication are essential skills.
Supporting Diverse Learning Styles
Every student is unique and has different learning preferences. Some may thrive on visual elements, while others prefer auditory or kinesthetic approaches. VR caters to this diversity by providing multisensory experiences that can accommodate various learning styles.
For instance, a literature lesson can be transformed by allowing students to enter the world of a novel’s setting, experiencing the story alongside the characters. Such immersive experiences enable students to connect with the material on a personal level, improving comprehension and retention.
The Future of VR in Education
As VR technology continues to evolve, its potential in education will only expand. While its implementation is still in its infancy, many schools and educational institutions are beginning to explore its capabilities. With decreasing costs and increasing accessibility, VR could soon become a staple in classrooms around the world.
Incorporating VR into teacher training programs is also essential, as educators must be equipped to leverage this technology effectively. Professional development programs can help teachers design VR experiences that align with curricular goals, ensuring students receive maximum benefits.
Conclusion
Virtual reality is revolutionizing the way educators approach teaching and learning. By making lessons engaging, interactive, and immersive, VR empowers students to take an active role in their education. As technology continues to advance, the possibilities for transforming education through virtual reality are endless.
FAQs
1. What equipment do schools need to implement VR in the classroom?
Schools typically need VR headsets, compatible computers or mobile devices, and VR educational content or software. Popular devices include Oculus Quest, HTC Vive, and Microsoft HoloLens.
2. Is virtual reality suitable for all age groups?
Yes, VR can be adapted for various age groups. Younger students might benefit from simpler experiences, while older students can engage with more complex simulations.
3. How can teachers create VR lessons?
Teachers can use existing VR content available through platforms like Google Expeditions or create custom lessons using tools like Engage or Unity. Professional development can enhance teachers’ skills in creating effective VR experiences.
4. Are there any potential downsides to using VR in education?
While VR offers many benefits, potential downsides may include costs, the need for teacher training, and concerns about motion sickness or discomfort during extended use.
5. How effective is VR in improving learning outcomes?
Early studies suggest that VR can enhance learning outcomes by improving engagement, retention, and understanding. However, more research is needed to fully understand its long-term effects on students’ academic performance.