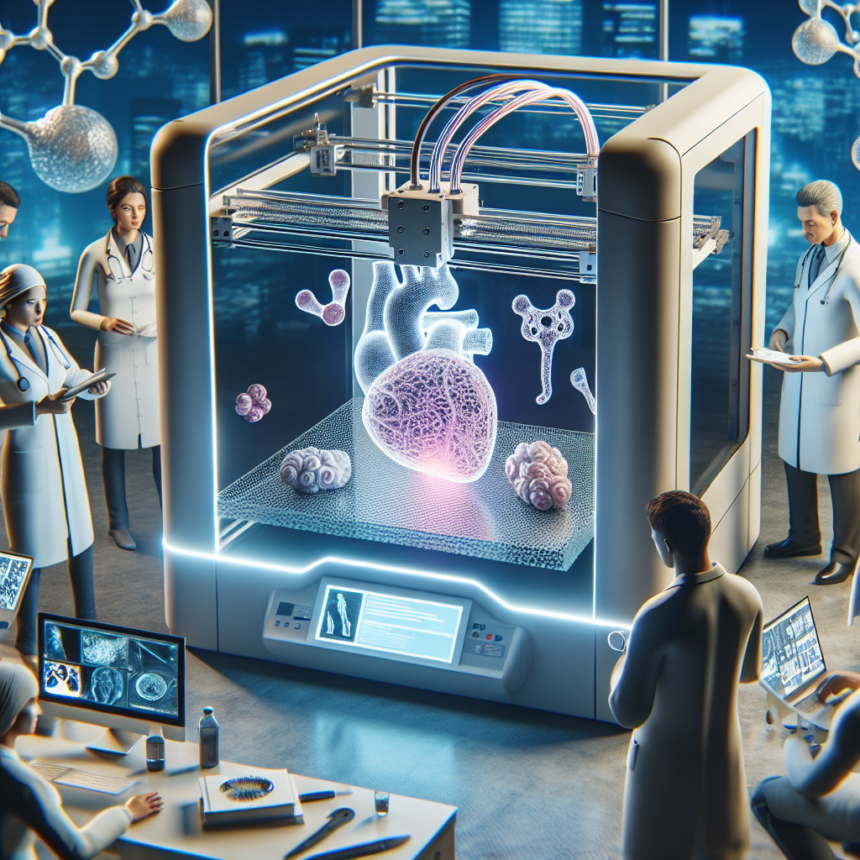
As technology continues to evolve, the impact on healthcare is becoming more profound, innovative, and life-changing. Among the standout advances in this sector is 3D printing, a technology that is revolutionizing the way medical treatment is delivered and personalized. From custom prosthetics to bioprinting tissues, this transformative technology is reshaping the landscape of medicine.
Customized Prosthetics and Orthotics
One of the most notable applications of 3D printing in healthcare is the production of customized prosthetics and orthotics. Traditional prosthetic fitting is often an uncomfortable and lengthy process. 3D printing allows for the creation of prosthetic limbs and devices that are tailored specifically to each patient’s anatomy and needs. This can significantly enhance comfort and functionality, leading to improved mobility and a better quality of life.
For instance, in 2014, a young boy named Alex Pring received a 3D-printed prosthetic arm that was designed to both meet his physical requirements and suit his personal tastes—customized with his favorite colors and patterns. This personalization not only provided Alex with a functional limb but also helped him develop confidence and a sense of identity.
Advanced Surgical Models
Another groundbreaking application of 3D printing in healthcare is the creation of advanced surgical models. Surgeons can use 3D-printed models of a patient’s anatomy prior to performing intricate procedures. This allows for better planning and more accurate execution in surgeries, ultimately leading to improved patient outcomes.
For example, surgeons can print replicas of organs or tumors based on CT or MRI scans, providing them with an accurate representation of the area to be operated on. This hands-on approach enables surgeons to rehearse complex procedures and identify potential complications beforehand, reducing the risks involved and enhancing patient safety.
Bioprinting and Organ Regeneration
While still in the experimental phase, bioprinting—the process of using 3D printing technology to create living tissues and organs—holds enormous promise for the future of medical treatments. The goal is to develop functional organs that can be transplanted into patients, potentially addressing the critical shortage of organ donors.
Researchers are making significant strides in creating simple tissues, such as skin and cartilage, using bio-inks that contain living cells. Success in this area could lead to printing more complex organs, reducing reliance on donors, and minimizing the risk of rejection since patients could have organs that are genetically matched to their own tissues.
Pharmaceutical Innovations
3D printing is also making waves in the pharmaceutical industry. The technology allows for the production of customized medications, engineered to meet the specific needs of individual patients. Dosing can be adjusted according to body weight or specific health conditions, leading to more effective treatments.
Moreover, 3D printing can facilitate the creation of multi-drug formulations, where multiple medications can be combined into a single pill. This can enhance patient adherence to treatment regimens, simplify the medication process, and potentially improve therapeutic outcomes.
Conclusion
The integration of 3D printing into healthcare is a revolutionary step that promises to enhance personalization, efficiency, and innovation in medical treatments. As clinicians, engineers, and researchers continue to collaborate, we can expect to see even more transformative applications in the coming years. The future holds a world where healthcare is not only accessible but tailored to meet individual needs, significantly improving patients’ lives.
FAQs
1. What is 3D printing in healthcare?
3D printing in healthcare refers to the use of additive manufacturing technologies to create medical devices, prosthetics, surgical models, and even biological tissues or organs. This technology allows for customization and rapid prototyping, resulting in innovative treatments and devices.
2. How does 3D printing improve prosthetics?
3D printing allows for the production of prosthetics that are tailored to fit the unique anatomy of each patient, offering improved comfort and functionality compared to traditional prosthetic methods. It also enables aesthetic customization.
3. Can 3D printing be used for organ transplants?
Yes, 3D printing, particularly bioprinting, is being explored for creating tissues and organs. Although still in experimental stages, advancements could lead to the development of functional organs for transplantation in the future.
4. What are the benefits of using 3D-printed surgical models?
3D-printed surgical models provide surgeons with accurate physical representations of a patient’s anatomy, allowing for better preoperative planning, rehearsal of complex surgeries, and minimizing surgical risks, ultimately improving patient outcomes.
5. Are 3D-printed medications possible?
Yes, 3D printing can be used to create customized medications tailored to individual patient needs, potentially improving efficacy and adherence to treatment regimens by allowing for personalized dosing and multi-drug combinations.